Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a spinal condition that affects millions worldwide, causing curvature and often discomfort or pain. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and exploring treatment options are crucial for those impacted by this condition. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of scoliosis, offering insights that can aid both patients and caregivers.
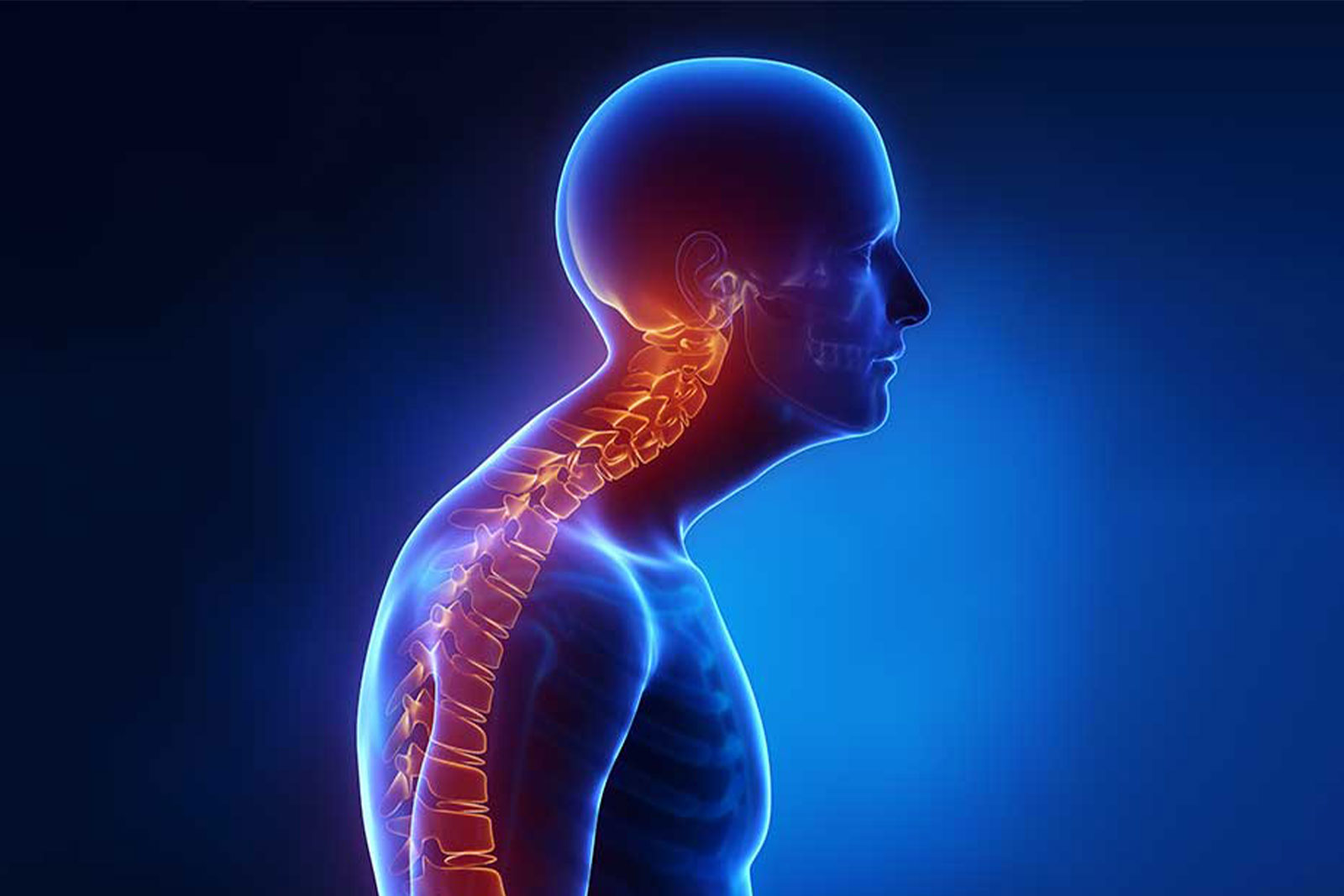
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine.Scoliosis can develop at any age, but it often becomes apparent during periods of rapid growth, such as adolescence. Treatment options for scoliosis depend on factors such as the age of the individual, the severity of the curvature, and whether the condition is progressing.
Types of Scoliosis:
- Idiopathic Scoliosis:
- Congenital Scoliosis:
- Neuromuscular Scoliosis:
This is the most common type of scoliosis, accounting for approximately 80% of cases. Idiopathic scoliosis occurs without a known cause, but researchers believe that genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors may play a role. Idiopathic scoliosis typically develops during adolescence, with the curvature often progressing during periods of rapid growth.
Congenital scoliosis is present at birth and results from abnormal spine development in the womb. This can occur due to vertebral malformations or abnormalities in the formation of the vertebrae, such as hemivertebrae (wedge-shaped vertebrae) or fused vertebrae. Congenital scoliosis is relatively rare but can lead to severe curvature and other spinal deformities.
Neuromuscular scoliosis develops as a secondary complication of neuromuscular disorders that affect muscle control and coordination. Conditions such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, spina bifida, or spinal cord injuries can lead to muscle weakness or imbalance, resulting in spinal curvature. Neuromuscular scoliosis tends to progress more rapidly and may be associated with other health complications.
Causes of Scoliosis:
- Idiopathic:
- Congenital:
- Neuromuscular conditions:
- Genetic factors:
- Connective tissue disorders
This is the most common form, where the cause is unknown. It typically develops during adolescence and is often discovered during routine school screenings.
Some individuals are born with scoliosis due to abnormal spinal development in the womb.
Conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy can lead to muscle weakness or imbalance, affecting spinal alignment.
There is evidence to suggest that scoliosis may run in families, indicating a genetic predisposition.
Conditions like Marfan syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which affect the connective tissues, can sometimes be associated with scoliosis.
Symptoms of Scoliosis:
Recognizing the symptoms of scoliosis is key to prompt diagnosis and treatment. These may include uneven shoulder heights, an asymmetrical waistline, or a noticeable curvature of the spine. Diagnosis often involves physical examination, followed by imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs to assess the severity and progression of the curvature. Early detection can prevent further complications and facilitate appropriate intervention strategies.
Treatments of Scoliosis:
Treatment for scoliosis depends on various factors, including the severity of the curvature, the age of the individual, and any underlying conditions. Mild cases may require only monitoring over time, while more pronounced curves may necessitate bracing or surgical intervention. Additionally, physical therapy and exercises tailored to strengthen the spine and surrounding muscles can play a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Prevent of Scoliosis:
- Practice Good Posture:
- Incorporate Core Strengthening Exercises:
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Prioritize Bone Health:
- Get Regular Check-ups:
Maintaining proper posture is essential for spinal health. Whether sitting, standing, or walking, strive to keep your spine aligned, shoulders back, and head held high. Avoid slouching or hunching over, especially for extended periods, as this can place unnecessary strain on the spine and contribute to misalignments over time.
A strong core helps stabilize the spine and reduce the risk of developing spinal abnormalities like scoliosis. Include exercises that target the core muscles, such as planks, bridges, and abdominal crunches, into your fitness routine. Strengthening the core not only supports spinal alignment but also improves overall balance and stability.
Sitting for long periods can contribute to poor posture and weaken the muscles supporting the spine. Take regular breaks to stand up, stretch, and move around throughout the day, especially if you have a desk job or spend extended hours sitting. Incorporate ergonomic adjustments to your workspace, such as using a supportive chair and positioning your computer monitor at eye level, to reduce strain on the spine.
Excess weight can place additional stress on the spine and increase the risk of developing spinal abnormalities. Aim to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise. Focus on consuming nutrient-rich foods and limiting processed foods and sugary beverages, which can contribute to inflammation and weight gain.
Strong bones are essential for supporting the spine and reducing the risk of osteoporosis-related spinal deformities. Ensure an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D through diet or supplements, as these nutrients play a critical role in bone health. Incorporate weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, or weightlifting into your routine to promote bone density and strength.
Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help identify any potential spinal issues early on and provide guidance on maintaining spinal health. Discuss any concerns or family history of spinal conditions with your doctor, who can recommend appropriate screenings or interventions as needed.
Nextwellness Treatment & Reasearch Center Pvt Ltd.
Plot no.298 apposite diamond garden, Near merwan cake shop,
Central avenue road Chembur east
MUMBAI 4000-71
Timing: 8 AM to 9 PM
Branch:- Chembur,Bandra.